It is known that the circadian clock in Drosophila can be sensitive to static magnetic fields (MFs). Man-made radiofrequency (RF) electromagnetic fields have been shown to have effects on animal orientation responses at remarkably weak intensities in the nanotesla range. Here, we tested if weak broadband RF fields also affect the circadian rhythm of the German cockroach (Blatella
Similar Posts
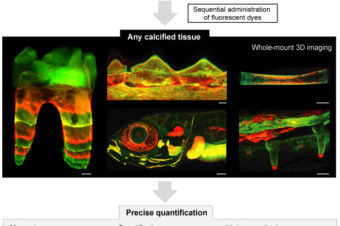
Spatiotemporal monitoring of hard tissue development reveals unknown features of tooth and bone development
Abstract: Mineralized tissues, such as bones or teeth, are essential structures of all vertebrates. They... Read More
Activity of Smurf2 Ubiquitin Ligase Is Regulated by the Wnt Pathway Protein Dishevelled
Cells 2020, 9(5), 1147. ABSTRACT Wnt and BMP signaling pathways are two key molecular machineries... Read More
The biocompatibility of polyaniline and polypyrrole 2: Doping with organic phosphonates
Conducting polymers (CP) can be used as pH- and/or electro-responsive components in various bioapplications, for... Read More
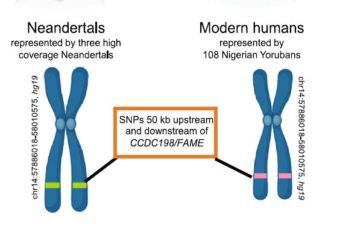
A previously uncharacterized Factor Associated with Metabolism and Energy (FAME/C14orf105/CCDC198/1700011H14Rik) is related to evolutionary adaptation, energy balance, and kidney physiology
Abstract: In this study we use comparative genomics to uncover a gene with uncharacterized function... Read More
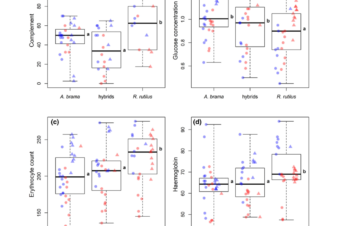
Vigour-related traits and immunity in hybrids of evolutionary divergent cyprinoid species: advantages of hybrid heterosis?
Abstract Hybrid advantage, described as the superiority of hybrids in some traits over their parents... Read More
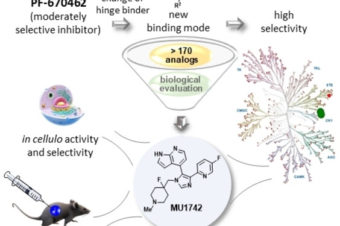
Discovery of Potent and Exquisitely Selective Inhibitors of Kinase CK1 with Tunable Isoform Selectivity
Abstract: Casein kinases 1 (CK1) are key signaling molecules that have emerged recently as attractive... Read More