It is known that the circadian clock in Drosophila can be sensitive to static magnetic fields (MFs). Man-made radiofrequency (RF) electromagnetic fields have been shown to have effects on animal orientation responses at remarkably weak intensities in the nanotesla range. Here, we tested if weak broadband RF fields also affect the circadian rhythm of the German cockroach (Blatella
Similar Posts
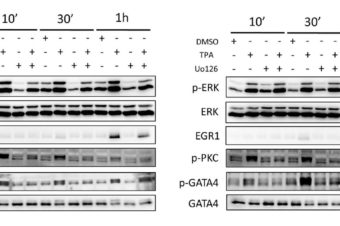
12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate increases cardiomyogenesis through PKC/ERK signaling
12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) is the most widely used diacylglycerol (DAG) mimetic agent and inducer of protein... Read More
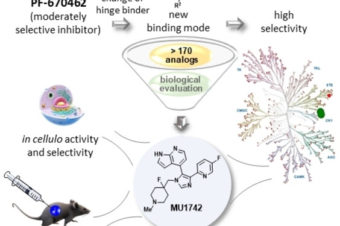
Discovery of Potent and Exquisitely Selective Inhibitors of Kinase CK1 with Tunable Isoform Selectivity
Abstract: Casein kinases 1 (CK1) are key signaling molecules that have emerged recently as attractive... Read More
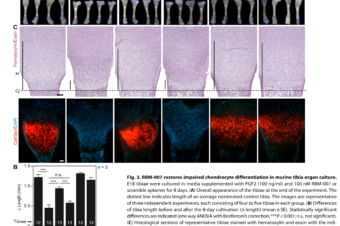
An RNA aptamer restores defective bone growth in FGFR3-related skeletal dysplasia in mice
Abstract: Achondroplasia is the most prevalent genetic form of dwarfism in humans and is caused... Read More
Bioactive Excreted/Secreted Products of Entomopathogenic Nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora Inhibit the Phenoloxidase Activity during the Infection
Insects 2020, 11(6), 353; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060353 ABSTRACT: Entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) are efficient insect parasites, that are... Read More
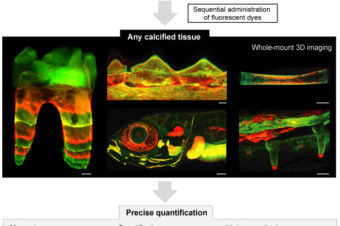
Spatiotemporal monitoring of hard tissue development reveals unknown features of tooth and bone development
Abstract: Mineralized tissues, such as bones or teeth, are essential structures of all vertebrates. They... Read More
Methodology for the Implementation of Internal Standard to Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis of Soft Tissues
Abstract: The improving performance of the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) triggered its utilization in the... Read More