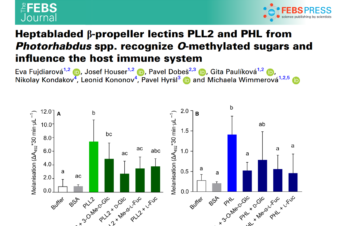
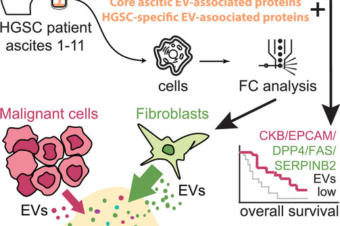
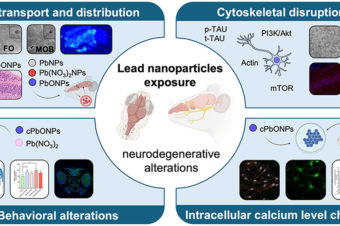
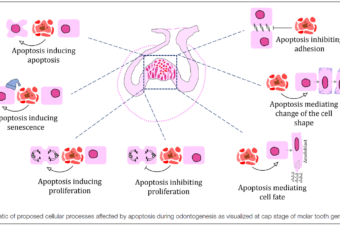
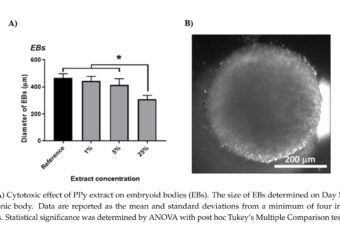
Abstract:
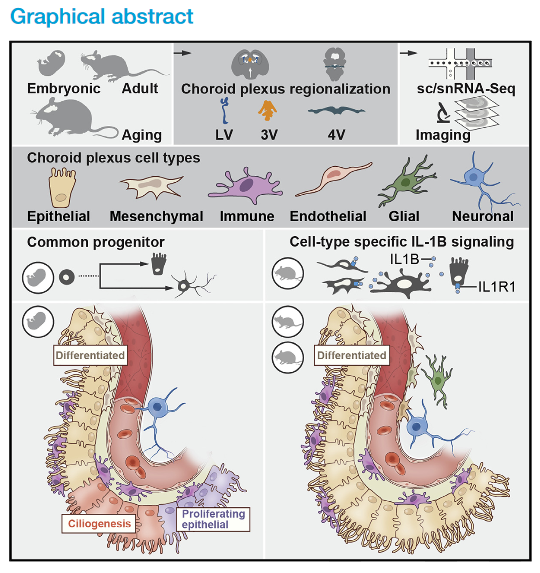
The choroid plexus (ChP) in each brain ventricle produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and forms the blood-CSF barrier. Here, we construct a single-cell and spatial atlas of each ChP in the developing, adult, and aged mouse brain.
We delineate diverse cell types, subtypes, cell states, and expression programs in epithelial and mesenchymal cells across ages and ventricles. In the developing ChP, we predict a common progenitor pool for epithelial and neuronal cells, validated by lineage tracing. Epithelial and fibroblast cells show regionalized expression by ventricle, starting at embryonic stages and persisting with age, with a dramatic transcriptional shift with maturation, and a smaller shift in each aged cell type. With aging, epithelial cells upregulate host-defense programs, and resident macrophages upregulate interleukin-1β (IL-1β) signaling genes. Our atlas reveals cellular diversity, architecture and signaling across ventricles during development, maturation, and aging of the ChP-brain barrier.
Authors:
Neil Dani 1, Rebecca Herbst 2, Cristin McCabe 3, Gilad Green 4, Karol Kaiser 5, Joshua Head 1, Jin Cui 1, Frederick Shipley 6, Ahram Jang 1, Danielle Dionne 3, Lan Nguyen 3, Christopher Rodman 3, Samantha Riesenfeld 3, Jan Prochazka 7, Michaela Prochazkova 7, Radislav Sedlacek 7, Feng Zhang 8, Vitezslav Bryja 5, Orit Rozenblatt-Rosen 3, Naomi Habib 9, Aviv Regev 10, Maria K Lehtinen 11
1 Department of Pathology, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
2 Klarman Cell Observatory, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA; Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
3 Klarman Cell Observatory, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA.
4 Edmond and Lily Safra Center for Brain Sciences, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 9190401, Israel.
5 Department of Experimental Biology, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno 611 37, Czech Republic.
6 Department of Pathology, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115, USA; Graduate Program in Biophysics, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02115, USA.
7 Czech Centre for Phenogenomics and Laboratory of Transgenic Models of Diseases, Institute of Molecular Genetics of the CAS, Prague 142 20, Czech Republic.
8 Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA; Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Chevy Chase, MD 20815, USA; McGovern Institute for Brain Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA; Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Department of Biological Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
9 Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA; Edmond and Lily Safra Center for Brain Sciences, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 9190401, Israel. Electronic address: naomi.habib@mail.huji.ac.il.
10 Klarman Cell Observatory, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA; Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA; Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Chevy Chase, MD 20815, USA; Koch Institute of Integrative Cancer Research, Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA. Electronic address: aviv.regev.sc@gmail.com.
11 Department of Pathology, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115, USA; Graduate Program in Biophysics, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02115, USA. Electronic address: maria.lehtinen@childrens.harvard.edu.