Dishevelled (DVL) is the key component of the Wnt signaling pathway. Currently, DVL conformational dynamics under native conditions is unknown. To overcome this limitation, we develop the Fluorescein Arsenical Hairpin Binder- (FlAsH-) based FRET in vivo approach to study DVL conformation in living cells. Using this single-cell FRET approach, we demonstrate that (i) Wnt ligands induce open DVL conformation, (ii) DVL variants that are predominantly open, show more even subcellular localization and more efficient membrane recruitment by Frizzled (FZD) and (iii) Casein kinase 1 ɛ (CK1ɛ) has a key regulatory function in DVL conformational dynamics. In silico modeling and in vitro biophysical methods explain how CK1ɛ-specific phosphorylation events control DVL conformations via modulation of the PDZ domain and its interaction with DVL C-terminus. In summary, our study describes an experimental tool for DVL conformational sampling in living cells and elucidates the essential regulatory role of CK1ɛ in DVL conformational dynamics.
Similar Posts
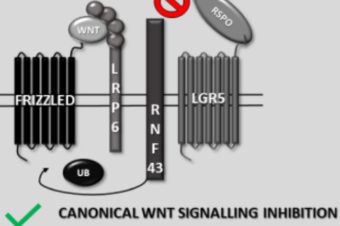
Protease Associated Domain of RNF43 Is Not Necessary for the Suppression of Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Human Cells
Another paper out and another step closer to a better understanding of #RNF43 tumor #suppressor... Read More
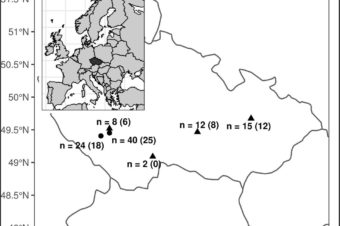
Differences in the growth rate and immune strategies of farmed and wild mallard populations
Individuals reared in captivity are exposed to distinct selection pressures and evolutionary processes causing genetic... Read More
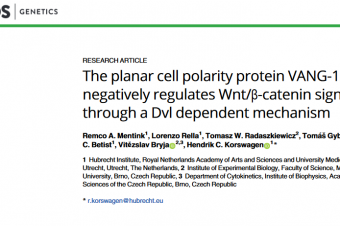
The planar cell polarity protein VANG-1/Vangl negatively regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling through a Dvl dependent mechanism
Van Gogh-like (Vangl) and Prickle (Pk) are core components of the non-canonical Wnt planar cell... Read More
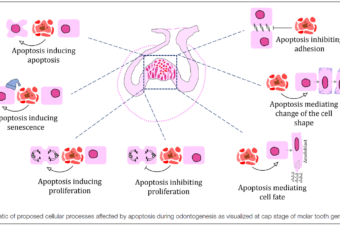
Role of Cell Death in Cellular Processes During Odontogenesis
Abstract: The development of a tooth germ in a precise size, shape, and position in... Read More
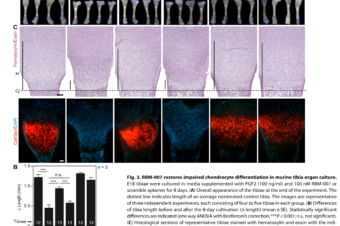
An RNA aptamer restores defective bone growth in FGFR3-related skeletal dysplasia in mice
Abstract: Achondroplasia is the most prevalent genetic form of dwarfism in humans and is caused... Read More
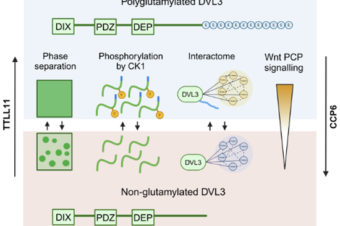
Carboxy-terminal polyglutamylation regulates signalling and phase separation of the Dishevelled protein
Abstract Polyglutamylation is a reversible posttranslational modification that is catalyzed by enzymes of the tubulin... Read More