It has been known for many years that in temperate climates the European honey bee,
Apis mellifera, exists in the form of two distinct populations within the year, short-living summer bees
and long-living winter bees. However, there is only limited knowledge about the basic biochemical
markers of winter and summer populations as yet. Nevertheless, the distinction between these two
kinds of bees is becoming increasingly important as it can help beekeepers to estimate proportion of
long-living bees in hives and therefore in part predict success of overwintering. To identify markers
of winter generations, we employed the continuous long-term monitoring of a single honey bee
colony for almost two years, which included measurements of physiological and immunological
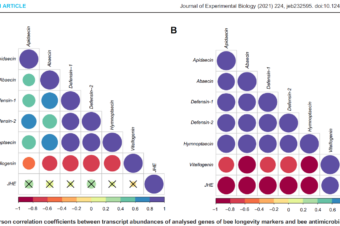
parameters. The results showed that the total concentration of proteins, the level of vitellogenin,
and the antibacterial activity of haemolymph are the best three of all followed parameters that are
related to honey bee longevity and can therefore be used as its markers.
Similar Posts
Winter honeybee (Apis mellifera) populations show greater potential to induce immune responses than summer populations after immune stimuli
Abstract: In the temperate climates of central Europe and North America, two distinct honeybee (Apis... Read More
Polarized Sonic Hedgehog Protein Localization and a Shift in the Expression of Region-Specific Molecules Is Associated With the Secondary Palate Development in the Veiled Chameleon
Secondary palate development is characterized by the formation of two palatal shelves on the maxillary... Read More
The effects of nano-sized PbO on biomarkers of membrane disruption and DNA damage in a sub-chronic inhalation study on mice
Although the production of engineered nanoparticles increases our knowledge of toxicity and mechanisms of bioactivity... Read More
Conducting composite films based on chitosan or sodium hyaluronate. Properties and cytocompatibility with human induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract: Novel composite films combining biocompatible polysaccharides with conducting polyaniline (PANI) were prepared via the... Read More
Sex differences and risk factors for bleeding in Alagille syndrome
Abstract: Spontaneous bleeds are a leading cause of death in the pediatric JAG1-related liver disease... Read More
Differences in the growth rate and immune strategies of farmed and wild mallard populations
Individuals reared in captivity are exposed to distinct selection pressures and evolutionary processes causing genetic... Read More