Abstract:
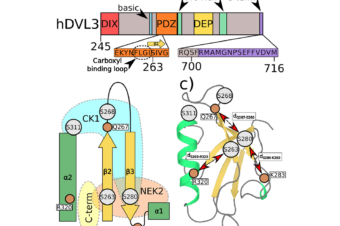
Over the past decades an extensive effort has been made to provide a more comprehensive understanding of Wnt signaling, yet many regulatory and structural aspects remain elusive. Among these, the ability of Dishevelled (DVL) protein to relocalize at the plasma membrane is a crucial step in the activation of all Wnt pathways. The membrane binding of DVL was suggested to be mediated by the preferential interaction of its C-terminal DEP domain with phosphatidic acid (PA). However, due to the scarcity and fast turnover of PA, we investigated the role on the membrane association of other more abundant phospholipids. The combined results from computational simulations and experimental measurements with various model phospholipid membranes, demonstrate that the membrane binding of DEP/DVL constructs is governed by the concerted action of generic electrostatics and finely-tuned intermolecular interactions with individual lipid species. In particular, while we confirmed the strong preference for PA lipid, we also observed a weak but non-negligible affinity for phosphatidylserine, the most abundant anionic phospholipid in the plasma membrane, and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. The obtained molecular insight into DEP-membrane interaction helps to elucidate the relation between changes in the local membrane composition and the spatiotemporal localization of DVL and, possibly, other DEP-containing proteins.
Authors:
Francesco L Falginella 1, Marek Kravec 2, Martina Drabinová 3, Petra Paclíková 2, Vítĕzslav Bryja 2 4, Robert Vácha 5
Affiliations:
1 CEITEC – Central European Institute of Technology, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic; National Centre for Biomolecular Research, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic.
2 Department of Experimental Biology, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno 62500, Czech Republic.
3 CEITEC – Central European Institute of Technology, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic.
4 Institute of Biophysics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i., Brno 612 65, Czech Republic.
5 CEITEC – Central European Institute of Technology, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic; National Centre for Biomolecular Research, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic; Department of Condensed Matter Physics, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kotlářská 2, 611 37 Brno, Czech Republic.